"The Promising Future of Cryptocurrency: Unlocking the Potential of Digital Money"
Cryptocurrency, the future's money, is revolutionizing the way we think about currency and transactions.
1. What is cryptocurrency and how does it differ from traditional money?
2. The Introduction of the First Cryptocurrency: Its Purpose and Impact
3. The Evolution of Cryptocurrency Value: A Look at Bitcoin and More
The value of cryptocurrencies has experienced significant volatility since their inception. Bitcoin, being the first cryptocurrency, has been at the forefront of this evolution. In its early years, Bitcoin had little to no monetary value. However, as awareness grew and more people started using it as a means of exchange or investment, its value began to rise. The price fluctuations were driven by factors such as market demand, regulatory developments, media attention, and overall investor sentiment. Bitcoin's price reached its all-time high in December 2017 when it surpassed $19,000 per coin. This surge was fueled by increased mainstream adoption and speculation by investors looking to capitalize on the rapidly growing market. Since then, Bitcoin's price has experienced several significant corrections and periods of consolidation. However, it has also shown resilience by consistently recovering from these downturns and reaching new highs over time. Apart from Bitcoin's evolution in value, numerous other cryptocurrencies have emerged with their own unique characteristics and use cases. Some cryptocurrencies aim to improve upon Bitcoin's limitations by offering faster transaction speeds (e.g., Litecoin), enhanced privacy features (e.g., Monero), or smart contract functionality (e.g., Ethereum). The evolution of cryptocurrency values showcases both the potential for substantial returns on investment and the risks associated with a volatile market. It also highlights the importance of conducting thorough research and understanding the underlying technology and fundamentals before investing in any cryptocurrency.
4. Advantages of Using Cryptocurrencies as a Form of Payment
5.1 Volatility
Definition
Volatility refers to the rapid and significant price fluctuations that cryptocurrencies experience within short periods of time. This unpredictability can be attributed to various factors such as market demand, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and investor sentiment.
Impact on Investors
The high volatility of cryptocurrencies presents both opportunities and risks for investors. On one hand, it allows for the potential of substantial gains in a short period of time. However, on the other hand, it also exposes investors to significant losses if they are not able to accurately predict or react to sudden price movements. To mitigate this risk, investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance and consider diversifying their cryptocurrency portfolio. Additionally, setting stop-loss orders or implementing trailing stop strategies can help limit potential losses by automatically selling a cryptocurrency if its price drops below a certain threshold.
5.2 Regulatory Uncertainty
Definition
Regulatory uncertainty refers to the lack of clear guidelines and regulations surrounding cryptocurrencies in many jurisdictions. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate these digital assets, leading to an ambiguous legal landscape.
Impact on Investors
The lack of regulatory clarity poses several risks for investors in cryptocurrencies. Firstly, it creates an environment where fraudulent activities such as scams and Ponzi schemes can thrive due to limited oversight. Secondly, sudden regulatory changes or crackdowns can significantly impact the value and liquidity of cryptocurrencies. Investors should stay informed about the regulatory developments in their respective jurisdictions and consider investing in cryptocurrencies that comply with existing regulations or have a higher likelihood of future compliance. Engaging with reputable exchanges that adhere to Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations can also help minimize exposure to regulatory risks.
5.3 Cybersecurity Threats
Definition
Cybersecurity threats refer to the risks associated with the vulnerability of cryptocurrency networks, wallets, and exchanges to hacking attacks, theft, and fraud. As cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks and rely on cryptographic algorithms for security, they can be attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Impact on Investors
5.4 Lack of Liquidity
Definition
Impact on Investors
Government Perspectives on the Future of Cryptocurrency
The government's perspective on the future of cryptocurrency varies across different countries. Some governments view cryptocurrencies as a potential threat to their national currencies and financial systems due to their decentralized nature and potential for facilitating illicit activities. These governments may impose strict regulations or even ban cryptocurrencies altogether. For instance, China has taken a hard stance against cryptocurrencies, banning initial coin offerings (ICOs) and cracking down on cryptocurrency exchanges. On the other hand, some governments recognize the potential benefits that cryptocurrencies can bring to their economies. They see cryptocurrencies as a way to foster innovation, attract investment, and promote financial inclusion. These governments often adopt a more lenient regulatory approach, seeking to strike a balance between consumer protection and fostering technological advancements. For example, countries like Switzerland and Malta have implemented favorable regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency businesses, attracting numerous blockchain companies to establish operations within their jurisdictions.
Financial Institutions' Perspectives on the Future of Cryptocurrency
List of Government Actions:
Banning or restricting initial coin offerings (ICOs)
Imposing strict regulations on cryptocurrency exchanges
Mandating Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures for crypto-related businesses
Introducing tax regulations for cryptocurrency transactions
Establishing regulatory sandboxes to foster innovation in the crypto industry
List of Financial Institutions' Actions:
Investing in blockchain technology for operational improvements
Exploring partnerships with cryptocurrency firms
Offering custodial services for cryptocurrencies
Developing blockchain-based payment solutions
Researching and developing their own digital currencies (e.g., central bank digital currencies)
These actions and perspectives from governments and financial institutions shape the future trajectory of cryptocurrencies, as they influence the regulatory environment, market acceptance, and overall adoption of digital assets.
Using Cryptocurrencies for Everyday Transactions
Cryptocurrencies are becoming increasingly popular as a means of everyday transactions. With the growing acceptance of digital currencies, individuals can now use them to buy groceries, pay bills, and more. This provides a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods such as cash or credit cards.
The Benefits of Using Cryptocurrencies for Everyday Transactions
There are several benefits to using cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions. Firstly, it offers greater security compared to traditional payment methods. Cryptocurrencies utilize advanced encryption techniques, making it extremely difficult for hackers to steal personal information or engage in fraudulent activities.
Secondly, using cryptocurrencies allows for faster and more efficient transactions. Traditional banking systems often involve lengthy processing times, especially when dealing with international transfers. However, with cryptocurrencies, transactions can be completed within minutes regardless of geographical boundaries.
How to Use Cryptocurrencies for Everyday Transactions
Set up a digital wallet: To start using cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions, you will need to set up a digital wallet. There are various types of wallets available online that cater to different needs and preferences.
Choose a cryptocurrency: Next, you need to choose which cryptocurrency you want to use for your transactions. Bitcoin is the most well-known and widely accepted cryptocurrency but there are also many others like Ethereum or Litecoin.
Make your purchase: Once you have found a merchant that accepts cryptocurrencies, simply select the items you wish to purchase and proceed to checkout. You will be provided with the necessary instructions to complete the transaction using your digital wallet.
In conclusion, cryptocurrencies have opened up a new world of possibilities when it comes to everyday transactions. With their enhanced security, faster processing times, and growing acceptance by merchants, using cryptocurrencies for buying groceries, paying bills, and more is becoming increasingly accessible and convenient for individuals around the world.
8.1 Increased Security and Transparency
8.1.1 Immutable Ledger
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the security and transparency of cryptocurrencies. One of the key features of blockchain is its immutable ledger, which ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or tampered with. This feature provides an added layer of trust and security to cryptocurrencies as it eliminates the need for intermediaries or trusted third parties to validate transactions. With a decentralized network of nodes verifying and recording transactions, the risk of fraud or manipulation is significantly reduced.
8.1.2 Publicly Verifiable Transactions
Benefits:
- Enhanced security: The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that transactions are secure and resistant to tampering. - Increased trust: The transparent nature of blockchain allows users to verify transactions independently, fostering trust within the cryptocurrency community. - Fraud prevention: Publicly verifiable transactions make it difficult for malicious actors to engage in fraudulent activities without being detected.
8.2 Decentralization and Elimination of Intermediaries
8.2.1 Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Blockchain technology enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. This decentralization aspect empowers individuals by giving them full control over their funds and eliminating reliance on centralized authorities.
8.2.2 Cost Reduction
By removing intermediaries from financial transactions, blockchain technology reduces costs associated with traditional banking systems, such as transaction fees, foreign exchange fees, and processing delays. This cost reduction makes cryptocurrencies an attractive alternative for individuals and businesses seeking more efficient and affordable financial solutions.
Benefits:
- Financial autonomy: Blockchain allows users to have complete control over their funds without relying on intermediaries. - Lower transaction costs: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain reduces transaction fees and other associated costs. - Faster transactions: Peer-to-peer transactions facilitated by blockchain technology are typically faster compared to traditional banking systems. Overall, the role of blockchain technology in the development and security of cryptocurrencies is crucial. It provides enhanced security, transparency, decentralization, and cost reduction benefits that contribute to the growth and adoption of cryptocurrencies across various industries.
1. Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the major challenges for widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies is the regulatory uncertainty surrounding them. Governments and financial institutions are still grappling with how to regulate and supervise this new form of digital currency. Without clear regulations, businesses and individuals may be hesitant to fully embrace cryptocurrencies due to concerns about legal compliance, tax implications, and potential risks.
Impact on Businesses
This regulatory uncertainty can have a significant impact on businesses that want to accept cryptocurrencies as a form of payment. They may face challenges in understanding and adhering to different regulatory frameworks in various jurisdictions. This can lead to additional costs for compliance measures and potential legal risks if they unknowingly violate any regulations.
Suggested Solutions:
Collaboration between governments, financial institutions, and cryptocurrency industry stakeholders to establish clear guidelines and regulations.
Education programs for businesses to understand the legal requirements and best practices when dealing with cryptocurrencies.
International coordination to create harmonized regulations that facilitate cross-border transactions involving cryptocurrencies.
2. Scalability Issues
Scalability is another limitation that needs to be addressed for widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies. As more people start using cryptocurrencies, the existing blockchain networks face challenges in processing a large number of transactions efficiently. Bitcoin, for example, has experienced scalability issues with long confirmation times and high transaction fees during periods of high demand.
Ethereum's Approach
Ethereum, one of the leading blockchain platforms, has been working on solutions like Ethereum 2.0 to improve scalability. This upgrade aims to introduce sharding, which will allow the network to process multiple transactions simultaneously by dividing the workload among different nodes.
Potential Solutions:
Implementing off-chain solutions like the Lightning Network, which enables faster and cheaper transactions by conducting them off the main blockchain.
Exploring alternative consensus algorithms that can enhance scalability without compromising security, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG).
Continued research and development to find innovative solutions for scaling blockchain networks while maintaining decentralization.
Regulations in the United States
In the United States, the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively involved in regulating initial coin offerings (ICOs), considering them as securities offerings subject to federal securities laws. Additionally, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) has classified cryptocurrencies as commodities and has oversight over cryptocurrency derivatives trading. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies as property for tax purposes, requiring individuals to report their cryptocurrency transactions and pay taxes accordingly. These regulations aim to protect investors and ensure compliance with existing financial laws.
Key Regulations:
- SEC's enforcement actions against fraudulent ICOs - CFTC's approval of Bitcoin futures contracts - IRS guidance on reporting cryptocurrency transactions
Regulations in Europe
European countries have taken different approaches when it comes to regulating cryptocurrencies. Some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, while others have expressed caution due to concerns about money laundering, terrorist financing, and consumer protection. The European Union has implemented the Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD5), which requires cryptocurrency exchanges and custodian wallet providers to comply with anti-money laundering regulations. Additionally, some countries like Switzerland have established a clear legal framework for cryptocurrencies, attracting numerous blockchain startups.
Key Regulations:
- AMLD5 requirements for KYC/AML compliance - Licensing frameworks for cryptocurrency businesses in Malta and Gibraltar - Regulatory sandbox initiatives promoting innovation in the UK
Regulations in Asia
Asia is a significant player in the global cryptocurrency market, but regulations vary widely across different countries. Japan has emerged as one of the most crypto-friendly nations, recognizing Bitcoin as legal tender and implementing a licensing system for cryptocurrency exchanges. South Korea has also taken steps towards regulation by introducing Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements for cryptocurrency exchanges. On the other hand, China has imposed strict regulations, banning initial coin offerings and shutting down cryptocurrency exchanges.
Key Regulations:
- Japan's licensing system for cryptocurrency exchanges - South Korea's regulations on KYC/AML for crypto exchanges - China's ban on ICOs and cryptocurrency exchanges
Increased Competition
The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced increased competition for traditional banking systems and financial institutions. Cryptocurrencies offer an alternative means of conducting financial transactions, which can be faster, more secure, and less costly compared to traditional banking methods. This has prompted banks and financial institutions to re-evaluate their business models and adapt to the changing landscape. They are exploring ways to integrate cryptocurrency technologies into their operations, such as offering crypto-related services or investing in blockchain-based solutions.
Disintermediation
One significant impact of cryptocurrencies on traditional banking systems is disintermediation. With cryptocurrencies, individuals can transact directly with each other without the need for intermediaries like banks. This bypasses the traditional banking system's role in facilitating transactions and managing accounts. As a result, banks may see a decline in their customer base for certain services like remittances or cross-border payments. To stay relevant, traditional banks may need to find new areas where they can add value beyond simple transaction facilitation.
Regulatory Challenges
The emergence of cryptocurrencies has posed regulatory challenges for traditional banking systems and financial institutions. Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks that are not under the control of any central authority or government. This lack of centralized control raises concerns about money laundering, fraud, and consumer protection. Regulators around the world are grappling with how to effectively regulate cryptocurrencies without stifling innovation or impeding legitimate use cases. Financial institutions must navigate these evolving regulations while ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
List:
- Increased competition from cryptocurrencies - Disintermediation as individuals transact directly - Regulatory challenges related to decentralized nature
Environmental Impact of Mining
Mining cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, requires a significant amount of computational power and energy consumption. This process involves solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. As a result, mining operations consume large amounts of electricity, leading to environmental concerns. The energy required for mining contributes to carbon emissions and increases the demand for fossil fuels.
E-waste Generation
Sustainability Concerns with New Cryptocurrencies
The creation of new cryptocurrencies also raises sustainability concerns due to their potential impact on resource consumption and electronic waste generation.
Resource Intensive Process
Developing a new cryptocurrency often requires extensive computing resources for tasks like coding, testing, and launching the network. These processes consume substantial amounts of electricity and computing power, contributing to carbon emissions.
Excessive Token Creation
In addition, some new cryptocurrencies are created through Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), where tokens are issued to investors. The proliferation of ICOs has led to a flood of new cryptocurrencies, many of which lack long-term viability or purpose. This excessive token creation not only strains computing resources but also contributes to market volatility and potential investor losses. To address these sustainability concerns, the cryptocurrency community can adopt practices such as conducting thorough feasibility studies before launching new cryptocurrencies. Additionally, implementing more stringent regulations on ICOs can help prevent the proliferation of unsustainable projects. By considering the environmental and sustainability aspects in the creation and mining processes of cryptocurrencies, the industry can work towards a more sustainable future that minimizes its ecological footprint and fosters responsible innovation.
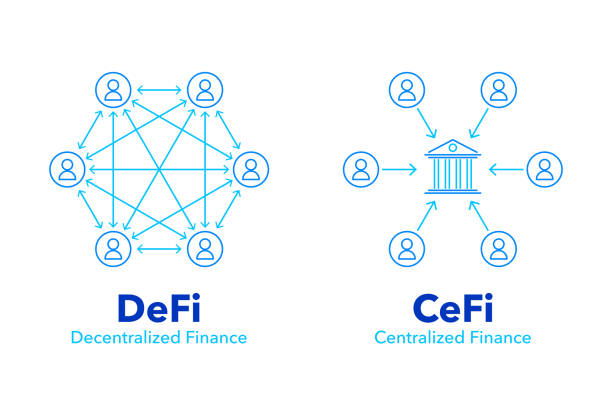
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance, also known as DeFi, refers to the use of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies to recreate traditional financial systems in a decentralized manner. Unlike traditional finance, which relies on intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions, DeFi platforms operate on smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) that enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. This allows users to have greater control over their funds, access financial services globally, and participate in various activities such as lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest.
Benefits of Utilizing Cryptocurrency in DeFi Platforms
1. Accessibility: By utilizing cryptocurrency in DeFi platforms, individuals from any part of the world can access financial services without the need for a traditional bank account. 2. Security: Cryptocurrencies are secured by cryptographic algorithms that make them highly secure against fraud or unauthorized access. 3. Transparency: Transactions conducted on DeFi platforms using cryptocurrencies are recorded on a public blockchain, providing transparency and immutability. 4. Lower Costs: Traditional financial systems often involve high fees for transactions or accessing certain services. DeFi platforms powered by cryptocurrencies can significantly reduce these costs. 5. Programmability: Smart contracts enable programmable money on DeFi platforms, allowing developers to create complex financial applications with automated rules and conditions. Overall, utilizing cryptocurrency in DeFi platforms brings numerous advantages such as increased accessibility, security, transparency, cost-effectiveness, and programmability to traditional financial activities.
1. Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. With blockchain, companies can securely track and verify every step of a product's journey, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing, distribution, and delivery. This ensures that products are authentic and not counterfeit, reduces the risk of fraud or tampering, and allows consumers to have complete visibility into the origins of the products they purchase.
Benefits:
- Enhanced transparency: Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency for all stakeholders involved. - Improved efficiency: By automating processes through smart contracts on the blockchain, supply chain management becomes more efficient with reduced paperwork and manual errors. - Increased trust: The immutability of blockchain records builds trust among participants in the supply chain network as it eliminates the possibility of data manipulation.
2. Blockchain in Healthcare
Potential Applications:
- Secure medical record sharing: Blockchain can enable patients to have control over their medical data while allowing authorized healthcare providers to access relevant information securely. - Drug traceability: Blockchain can ensure the authenticity and integrity of pharmaceuticals by creating an immutable record of each step in the supply chain process. - Streamlined insurance claims: Smart contracts on a blockchain could automate insurance claim processes by verifying policy details and triggering payments based on predefined conditions.
3. Blockchain in Voting Systems
Possible Advantages:
- Immutable voting records: Blockchain creates a permanent record of each vote that cannot be altered or manipulated. - Increased voter participation: With secure online voting platforms built on blockchain, accessibility to voting can be improved, potentially increasing voter turnout. - Enhanced trust in election results: The transparency and auditability provided by blockchain technology can help restore trust in electoral processes. Note: These paragraphs are for illustrative purposes only and should be expanded further with more detailed information if required.
Conclusion:
Summary
"The Promising Future of Cryptocurrency: Unlocking the Potential of Digital Money" The cryptocurrency market is currently experiencing significant growth and development. Bitcoin, the first and most popular cryptocurrency, has played a crucial role in shaping this industry. Ethereum, another prominent cryptocurrency, offers unique features and benefits. Altcoins differ from Bitcoin and Ethereum in various ways. While some believe that cryptocurrencies have the potential to replace traditional fiat currencies in the future, there are also risks and challenges associated with investing in them. Governments and regulatory bodies are responding to the rise of cryptocurrencies by implementing regulations. Various industries are embracing cryptocurrency technology for real-world applications.
THANKS FOR YOUR TIME LEARNING















Comments
Post a Comment